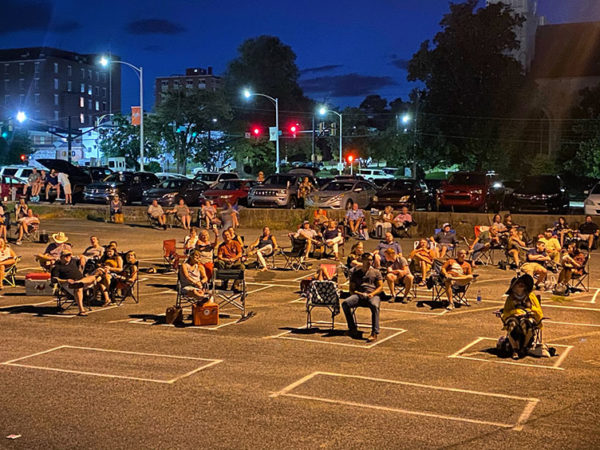
This past weekend the Macon Film Festival held one of their few live screenings of this year in my theater. (The rest of the festival content is being streamed.) They showed The Sound of Identity, a documentary about the first opera performance by a trans person in the U.S. The singer, Lucia Lucas, is an American living in Germany who was invited to perform Don Giovanni for Tulsa Opera in their 2018-2019 season. The angle they were taking is that Don Giovanni is a master of disguise and uses that in the process of his seductions.
The movie is basically what you want a film on this subject to be. Despite the PR text about Oklahoma being one of the reddest parts of the United States and the artistic director, Tobias Picker’s line in the trailer about potentially needing to resign, the socio-political elements of Tulsa never factor in. (They do have some fantastic shots of the city.) The movie could have happened anywhere, it just so happens Tulsa invited Lucas first. Similarly, the general approach of the movie was that this was a production of Don Giovanni where the lead just happened to be a trans person.
Because in fact, the movie is really about us –the arts profession. I am not alone in feeling this. I had a conversation with my marketing director and she remarked, unprompted, how much the movie was about arts administration. The biggest conflicts arise from things we deal with every day regardless of what the show is and who is performing. Their bad dress rehearsal moment is when the singer playing Leporello, a major part, gets sick and the assistant director does the blocking while the guy playing Commendatore sings the part, all of which makes it difficult for Lucas to synch up properly.
This is actually a good movie to show people who aren’t familiar with mounting a production because there is a lot of detail, but very little technical jargon. Though certainly I may be assuming a lot of shared basic knowledge from my long career in the arts.
Pretty much everything we discuss about running an arts organization is in this movie. The whole opera is dying and tickets only cover a portion of the $500,000 cost it takes to mount a production conversation occurs. (Their revenue goal was $120,000. We never hear the final tally, but sales were at ~$70,000 a few weeks out.)
Lucas and the artistic director have a conversation about how a trans person in the lead will attract a new audience and some of those they talk to say that is the reason they are attending. (With one guy it seemed pretty clear he didn’t anticipate coming back for other productions.)
There is a discussion about the need for board diversity. A representative for Tulsa Opera touts the board diversity, but the interviewer actually says he has to push back on that statement because the board of 30-50 (per the movie) has only two people of color. The representative backpedals a little saying there are a large number of homosexuals on the board.
There is a fair portion of the movie associated with promoting the production which illustrates just how much time is involved and how difficult it can be to do it well.
Between the organization and Lucas’ own drive, the singer is shown doing a lot of social gatherings. That comes up as a potential problem in a conversation with the director when Lucas says she isn’t feeling the guidance the director is giving with a particular song. The director says Lucas needs to conserve her energy and not do so many public appearances that she feels drained during rehearsals.
Lucas also prints up promotional postcards on her own dime and goes out to a park to hand them out. The artistic director accompanies her, but isn’t happy with what is happening. When they interview him alone, he says something akin to “I don’t want to characterize it as a fiasco, but it was sort of a fiasco.”
There was a moment in a restaurant that made me cringe a little where Lucas and the artistic director are eating and strike up a conversation with one of the restaurant staff. They tell her they are doing Don Giovanni and ask her if she knows the show. The staff member says she hasn’t heard of it and then Lucas says, “well here is the score.” Then they end the conversation telling her to tell anyone who asks that they are doing the opera. I didn’t feel like that exchange advanced the staff person’s knowledge or incentive to attend much at all.
Which is not to say that Lucas wasn’t able to have constructive conversations about the opera or her career because she was shown chatting at least a half dozen social gatherings. Near the end of the movie, she says she wants people to leave the opera hating Giovanni, but also loving him, but hating themselves for loving him because he represents misogyny and sexual predation in an extreme. Something like that would get people wanting to know more.
Ultimately, there is a scene where Lucas says she has been told that it is not her job to worry about how well the show is selling and has been asked to scale back her activities.
You are probably getting the sense that there is very little sensationalism about the lead in this opera being a trans person. So much of the movie is pretty run of the mill as far as productions go, but also relatable for people who aren’t in the arts world. Lucas has been a huge video game fan since she was younger. We see her playing video games while rehearsing in her room as a way to disconnect her brain. She also draws a parallel between being able to play Magic: The Gathering online versus playing in person to the experience of watching arts online being no substitute for experiencing it live in person.
There is a section where Lucas and the artistic director, Tobias Picker, are playing a Mario Brothers game where Picker talks about the challenges of his career as a composer and being married in the Supreme Court by Ruth Bader Ginsberg who is a fan of his work. The conversations between Lucas and Picker are some of the best moments of the movie.
The director of the opera, Denni Sayers, has some good moments waxing philosophical about art and celebrity–kids today want to be famous, but can’t answer when you ask what they want to be famous for when there are so many things to be involved with from politics, racial justice, environment, science, arts, etc.
As I said, the movie is really about arts organizations and the environment in which they operate. If you have an opportunity to see the movie, I think you will enjoy it. Right now it is playing a few film festivals, but the producers alluded to an ability to stream it that will be announced soon.










Thanks. Your explanation provides a lot of clarity on the concept that I was missing. Even as I wrote it,…