Over the last week you may have seen mention that after 10 years in existence, Createquity will be ceasing operations at the end of the 2017 calendar year.
This is a great pity. One of the goals founder Ian David Moss had as he developed his blogging project into a think tank was to facilitate arts administrators’ ability to understand research findings since they so often didn’t have the opportunity to review, much less finish research reports. Just last week, I cited one of his recent entries as the basis for a post.
It will probably come as no surprise that difficulty finding suitable funding for Createquity’s efforts is the basis for the decision to cease operations. Ian discusses all the options they weighed and opportunities of which they tried to avail themselves. Ultimately, in summary he says,
These are among the reasons why the arts field has, since the 1980s, dug a formidable graveyard for failed think tank initiatives, some of which have become so buried under the weight of history that I only learned about them for the first time earlier this year.
The project I most regret seeing fall by the wayside is their effort to chart what we know about the benefits of the arts in improving lives. Createquity graphed out research studies about the benefits of the arts on a scale that indicated the quality of the evidence and whether the research said a benefit existed. This information is extremely important to know if you are going to advocate for arts and culture and cite research findings. Looking at Createquity’s evaluation, the evidence that supports commonly made assertions about the benefit of arts in educational and social outcomes is weaker than it is made out to be or there is a lack of corroborating research.
Think about it this way. TV news programs often have short segments where they talk about the amazing benefits of dark chocolate, red wine, acai berries, etc., but when you take the time to really examine the evidence you discover you would have to consume three times your body weight daily to realize those benefits.
Funding for arts and culture entities is already tenuous as it is, (to whit, Createquity), the sector doesn’t need to have people denouncing it for making overblown claims. (And as I have often argued, we shouldn’t be invoking the utilitarian value of the arts to justify it anyway.)
There the end of his post, Moss talks about the preparations they are going through over the next few months. They will be publishing summary articles about the work they have done. (One on cultural equity was published today.)
They intend to make their work available to anyone who might wish to continue where they are leaving off.
Over the next couple of months, we will be polishing up our internal training materials and resources to make it as easy as possible for people in the arts community to carry on aspects of the work we’ve started in their own spaces and in their own names. And in November and December, you can expect to see some parting thoughts from our team to philanthropists and researchers seeking to optimize their investments in the arts in the decade ahead. Our goal in all of this is to activate the latent potential of our work over the past ten years into the most accessible and actionable content possible.
I think there are many who join me in hoping that someone will be able to continue the important work they have started.









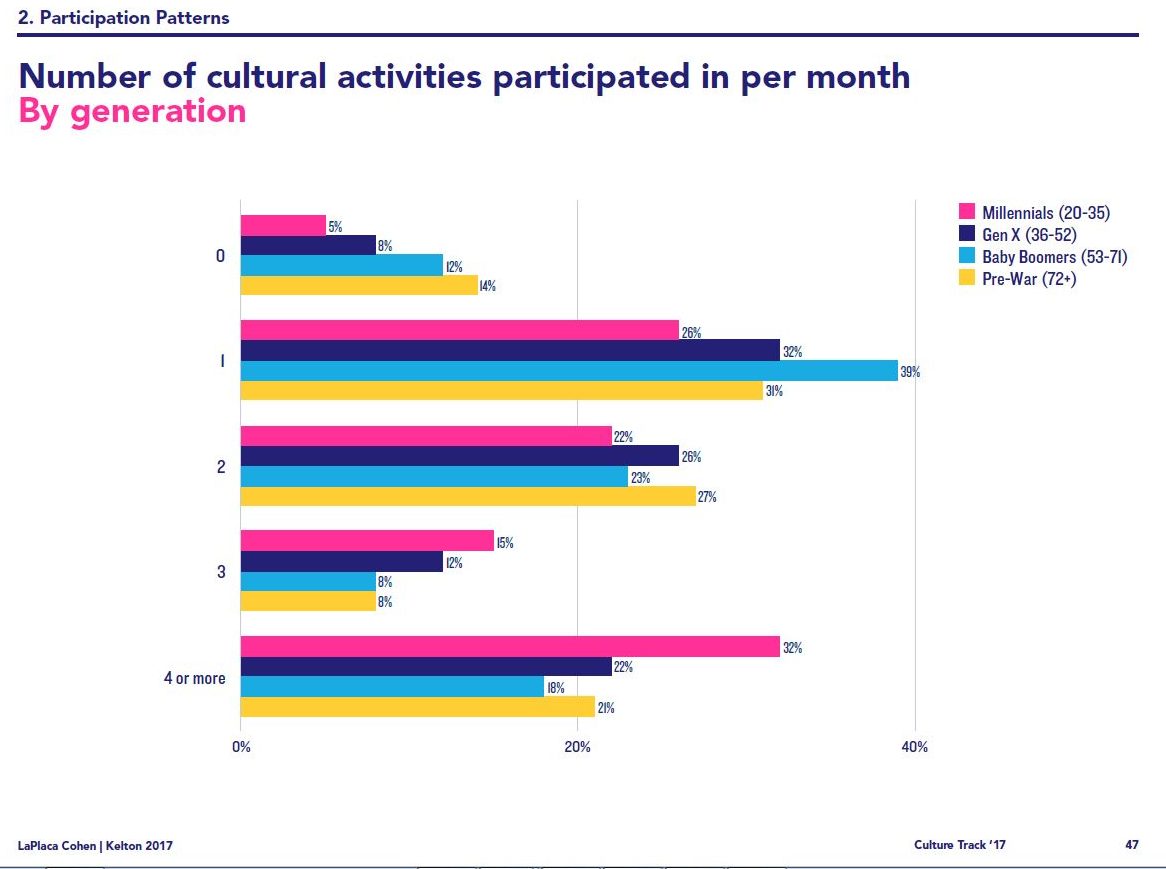

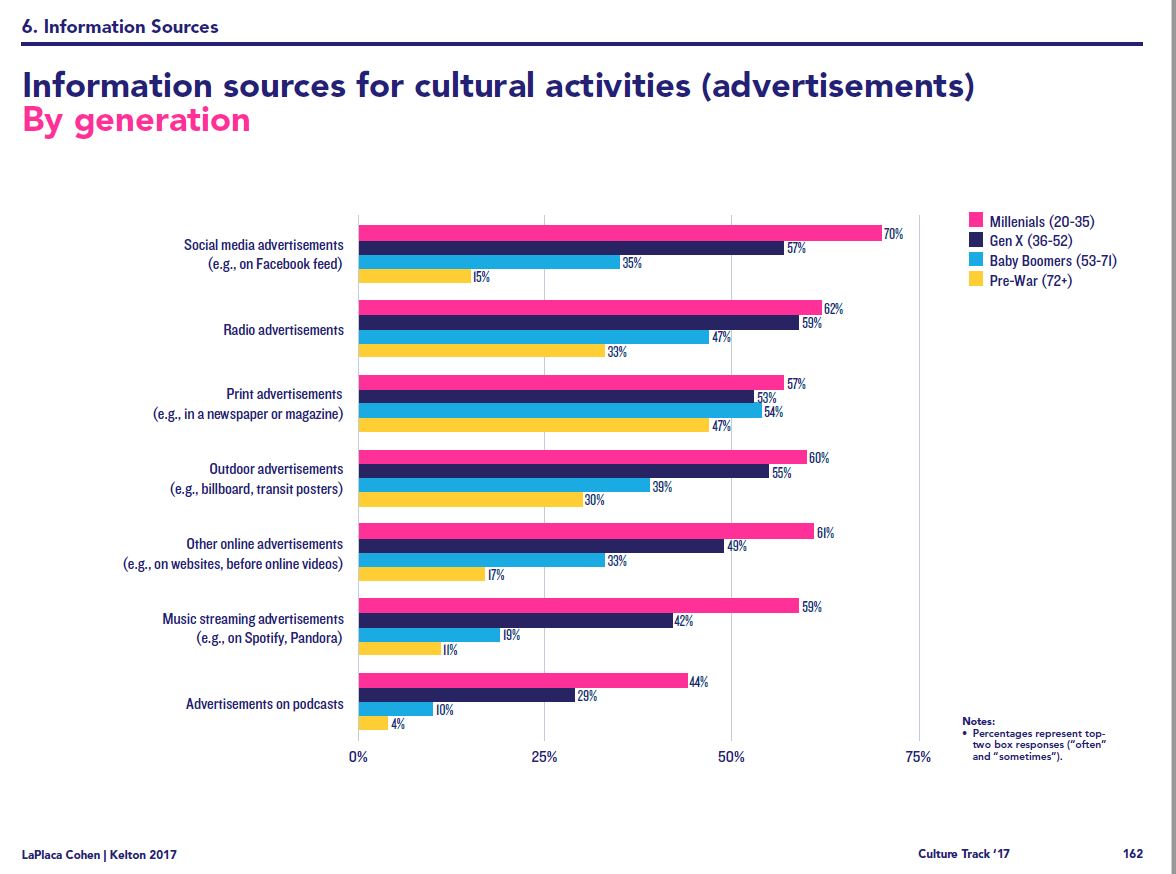
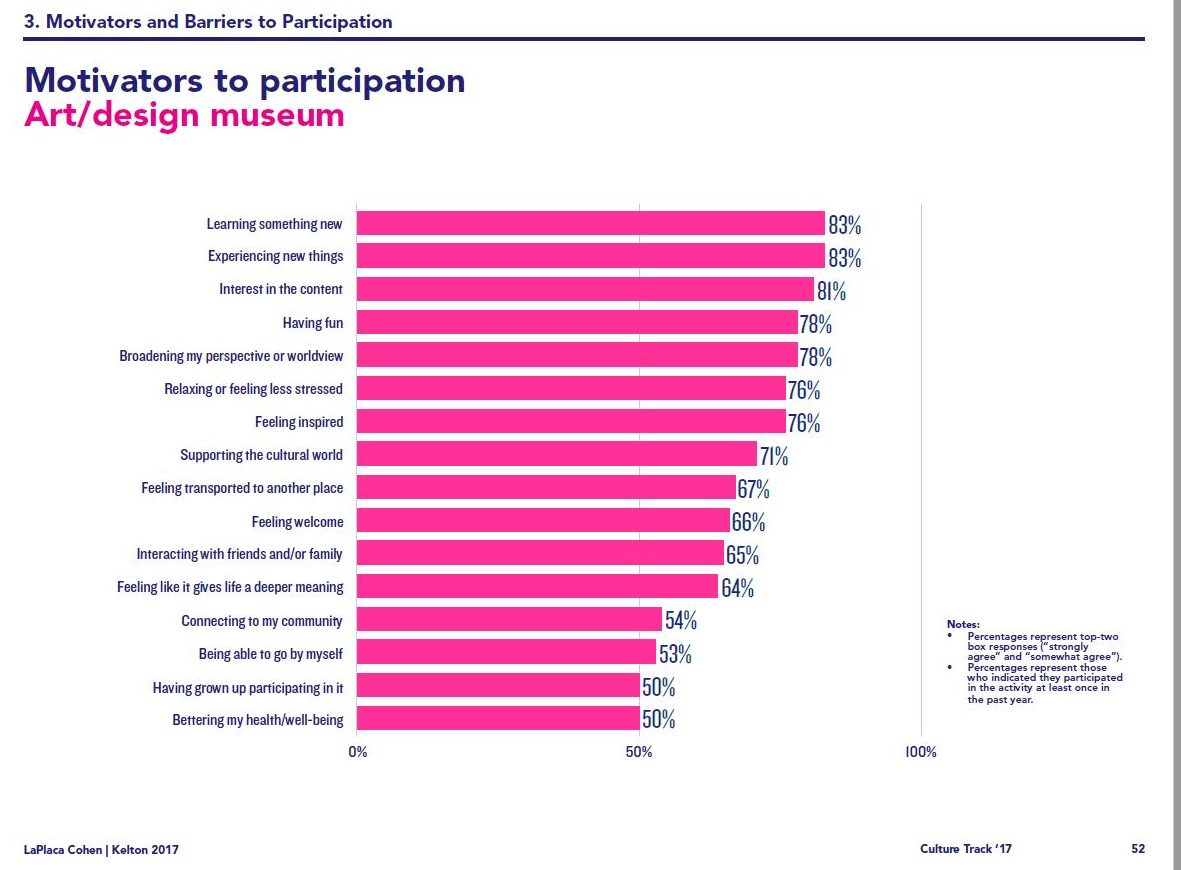
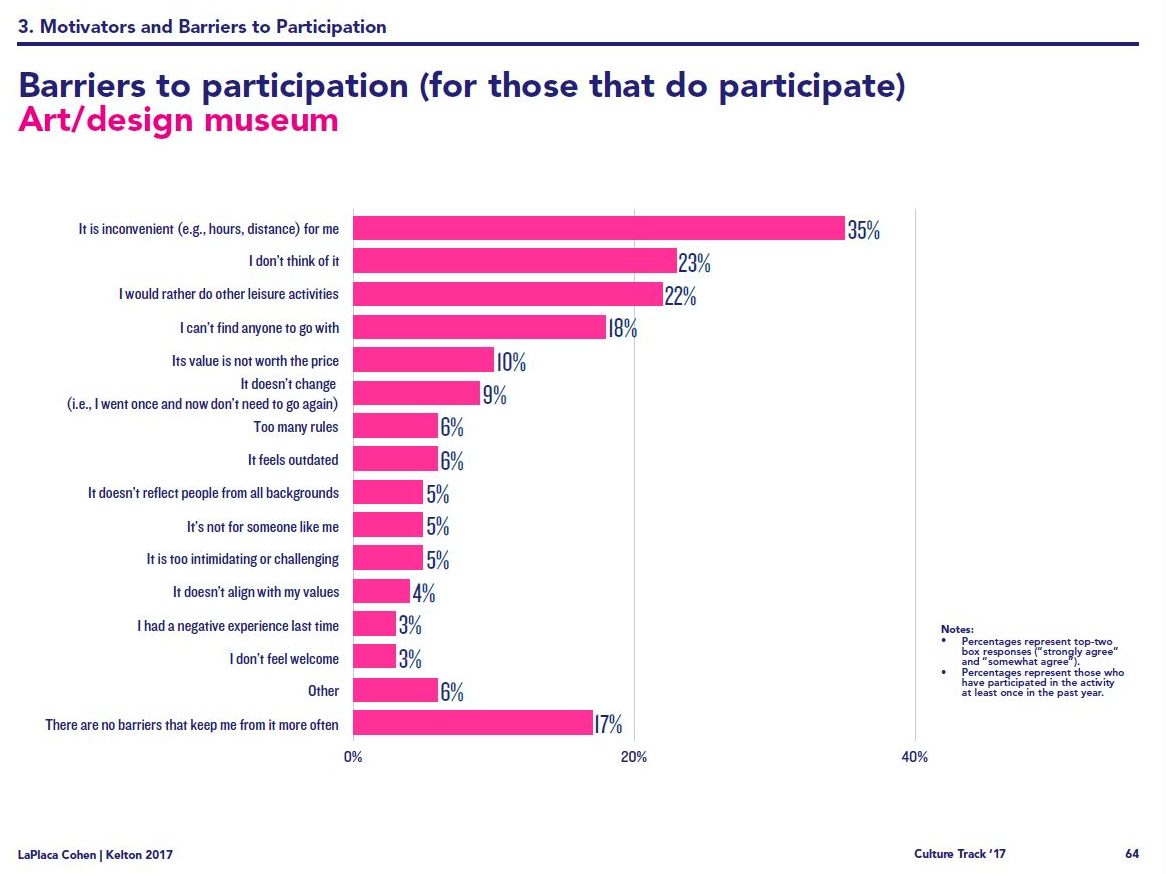




Santa Cruz Shakespeare has several tiers of benefits for donors/members. Some, like season-announcement parties, are open to several tiers. Some,…