Daniel Pink made a tweet today that I immediately bookmarked so I could go back to it.
I hadn’t noticed at the time that this was year-end summary type article that reviewed the best advice entrepreneurs had given in 2020. There are a lot of interesting bits of insights covered here, some of which are more applicable to arts organizations than others.
The “What Would Your Replacement Do?” question referenced in Pink’s tweet was one of those with broad application. It refers to a mental exercise Upstart co-founder Dave Girouard would use to keep himself from getting too complacent:
…what would happen if tomorrow my board got together and fired me,” says Girouard….And if they bring her in and she starts at Upstart — what would she do differently than what I’m doing? I think about that for a while, and then I tell myself, ‘Why the hell aren’t you doing those things?’ It’s just this weird game I play to get myself to recognize that while I’m doing some things okay, I can be lulled into a place of feeling good about myself when I’m probably not doing some other things very well.”
The first bit of advice on the list caught my eye because it was a list of 40 questions to ask on interviews. The list is obviously written for the commercial sector and pretty heavily geared for start-ups there were still quite a number that would easily suit non-profit arts.
Things like: “What’s something that would only happen here but wouldn’t at other organizations?”, “When you’ve done your best work here, what about the culture has enabled you to do that?”, “What would 1:1’s be like with my direct manager? What types of topics would we discuss?”, “What is the title of the most senior underrepresented person at the company?”
“If I asked your investors what they’re worried about, what would they say?” –this one caught my attention because I immediately thought to replace “investors” with “board” which got me thinking about how well the organization might be communicating issues with the board and if the board was paying attention.
An article about Job To Be Done (JTBD) also caught my attention based on the statement: “People don’t simply buy products or services, they ‘hire’ them to make progress in specific circumstances.” This is often the case with people and arts and cultural experiences. People value the experiences across multiple dimensions.
Sunita Mohanty, who was interviewed for the article said she often uses the following prompt in relation to product development.
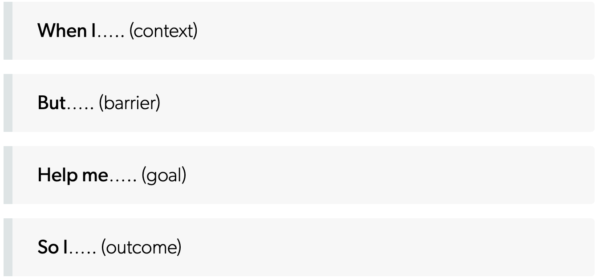
Which she says translates into the following: “Peloton JTBD: When I need an option to workout, but I can’t go to my favorite studio, help me to get a convenient and inspiring indoor workout, so I can feel my best for myself and my family.”
Off the top of my head, the way this might translate for an arts situation might be: “When I am seeking opportunities to spend time connecting with my family and friends, but I have trouble identifying places we feel completely welcomed, help us see ourselves and our stories so we feel acknowledged and valued in the broader community.
There is a lot of really valuable advice about hiring, evaluation, office culture, and diversity and inclusion listed in the article. As tempted as I am to cover them all, I don’t want to make this post super long. Many of the ideas intersect with other posts I have made or other articles that are out there.
But one idea that never came to my attention before was use of asynchronous video tools as a form of communication and new hire training.
In the early days of building Drift, I was using WhatsApp all the time. It was easy to record and send videos quickly. And so I started to communicate to my senior leadership team mostly asynchronously through video and audio messages,” says Cancel. “If we have a problem, we’d make a quick video on what we sucked at, how we fixed it, the results, and what we learned.
[…]
But Cancel has also noticed other benefits. “It allowed me to really think through what I was saying, versus just getting in a room with someone or having a back and forth in text messaging or a phone call,” he says. “It was the sharing aspect that really made it an effective tool for us — all of a sudden we had old videos on different topics that we could share with people who were starting their journey at Drift in their onboarding process…getting everyone focused, and helping folks understand why we were making decisions, giving us an ability to be transparent in a way that we couldn’t before.”
Given that so many people feel comfortable making videos of every little move they make, this struck me as a pretty viable practice in arts organizations and one that might even inform creative works.



Thanks for what you are doing to bring cultural change to the arts. It is so important to represent everyone.…